Linear Equation Ymx+c
Nimit Kumar Singh Only transformations of the form y = mx are linear Let me demonstrate why this is not a a linear transformation Using equation (1), f (x1x2) = m (x1x2) c = mx1 mx2 c = (mx1 c) (mx2 c) c = f (x1) f (x2) c != f (x1) f (x2).
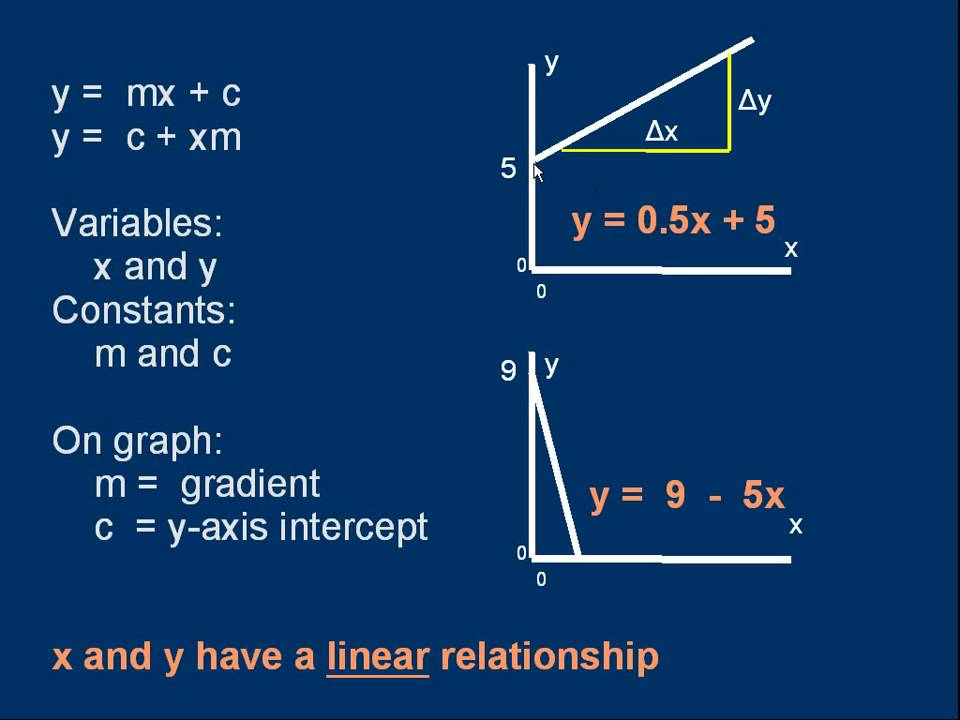
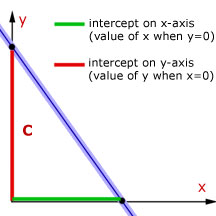
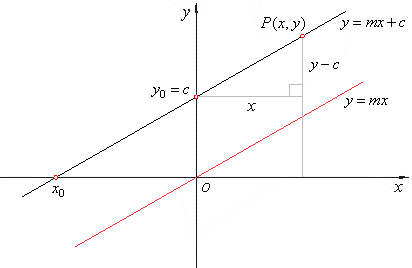
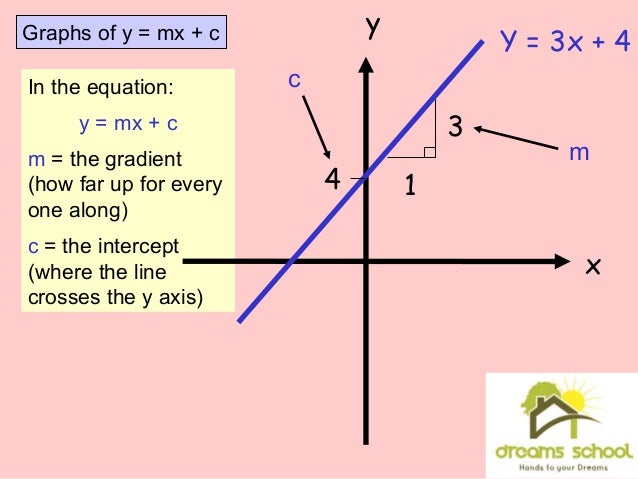
Linear equation ymx+c. The equation of a straight line on a graph is made up of a y term, an x term, and a number and are written in the form of y = mx c The slope of the line is known as the gradient and is represented by m in the equation The point at which the line crosses the yaxis is the c in the equation. Where A, B, and C are constants Also, the variable may be different from x Thus we should not get too locked into always seeing an x there Source enwikipediaorg Steps to Solve Linear Equations If a=b then ac = bc for any c. Whatever the original form of a linear equation, it is often helpful, especially for graphing, to have the equation rearranged into "y=" form Solving a linear equation in two variables for y= is a type of literalequation solving Here's how it works Find the slope of the line with equation 3x 2y = 8.
Linear Equation Formula is given by y = mx c Where x and y are two variables, c is a constant and m is the slope of the equation Solved Examples Using Linear Equation Formula. For a linear function is y = mx b, Where m = the slope , x = the input variable (the “x” always has an exponent of 1, so these functions are always first degree polynomial ) b = where the line intersects the yaxisUnit 3 Linear Functions Equations And Their Algebra –. The Textbook Exercise on the equation of a line y=mxc Videos, worksheets, 5aday and much more.
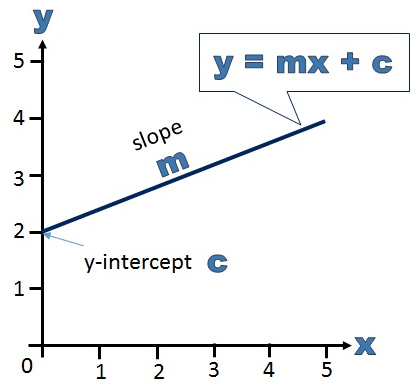
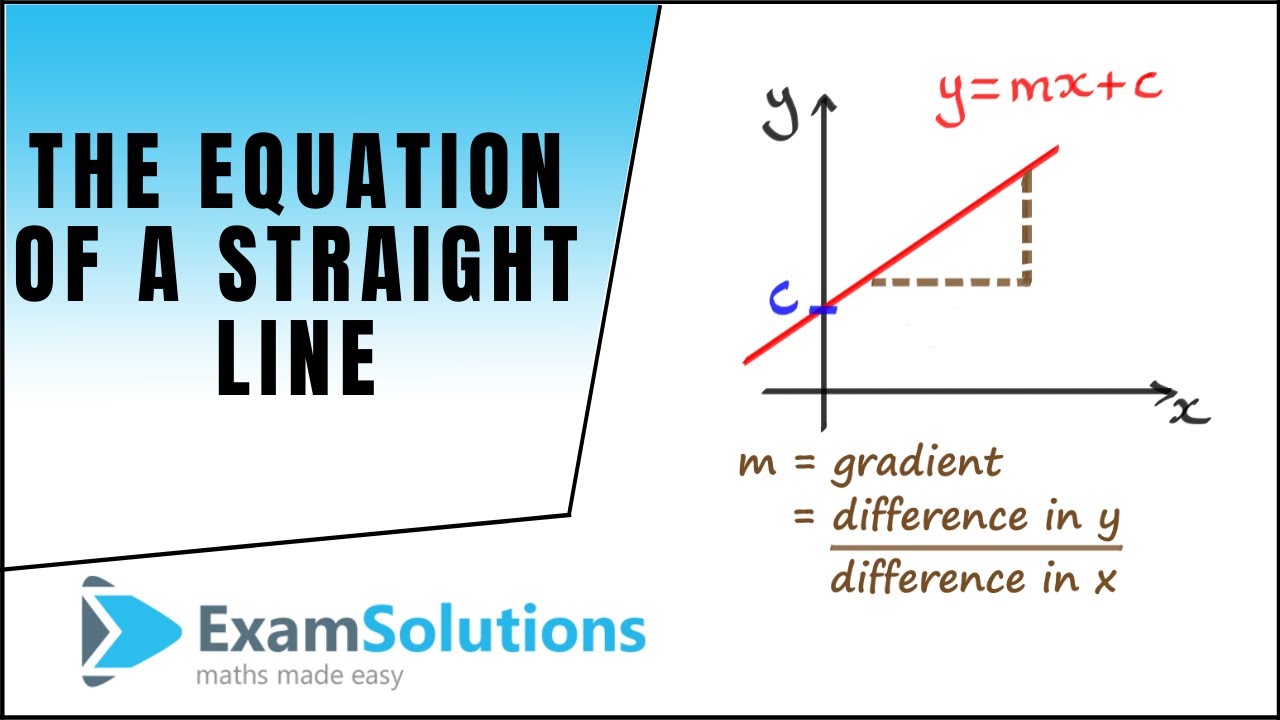
Linear equations are equations of the first order These equations are defined for lines in. One variable Frequently the term linear equation refers implicitly to the case of just one variable In this case, the equation can be put in the form =, and it has a unique solution = − in the general case where a ≠ 0In this case, the name unknown is sensibly given to the variable x If a = 0, there are two casesEither b equals also 0, and every number is a solution. This is a linear function showing a relationship between x and y For y = mx c, we have y expressed as a function of x, whereby any increase in x is calculated to be an (m times x) increase in y The c value is the value of y when x = 0 If this function is graphed as a line, m is the slope of that line and c is the yintercept.
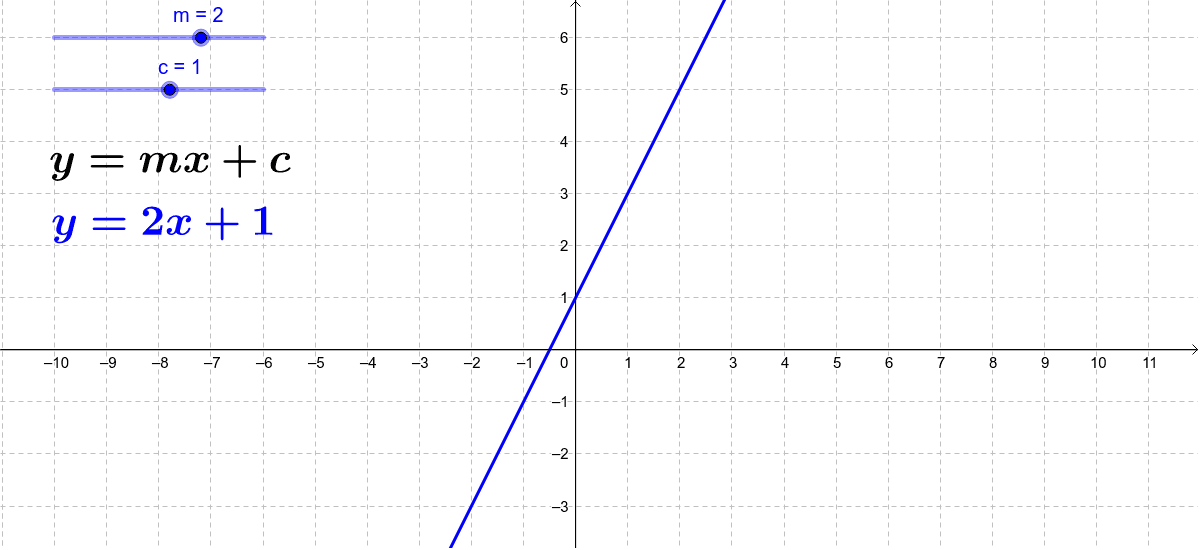
One variable Frequently the term linear equation refers implicitly to the case of just one variable In this case, the equation can be put in the form =, and it has a unique solution = − in the general case where a ≠ 0In this case, the name unknown is sensibly given to the variable x If a = 0, there are two casesEither b equals also 0, and every number is a solution. M = yx b m = m = – b m = y –. Linear equation (y = mxb) Click 'reset' Click 'zero' under the right b slider The value of m is 05 and b is zero, so this is the graph of the equation y = 05x0 which simplifies to y = 05x This is a simple linear equation and so is a straight line whose slope is 05 That is, y increases by 05 every time x increases by one.
Graphing linear equations, when the equation is given in the slopeintercept form (y = mx b) graphing linear equations, when the equation is given in the normal form (Ax By C = 0) graphing lines, when the slope and one point on it are given;. Graphing a linear equation written in slopeintercept form, y= mxb is easy!. But note that, most linear equations will not start off in this form Straight line equation in coordinate geometry is” y = mx c;.
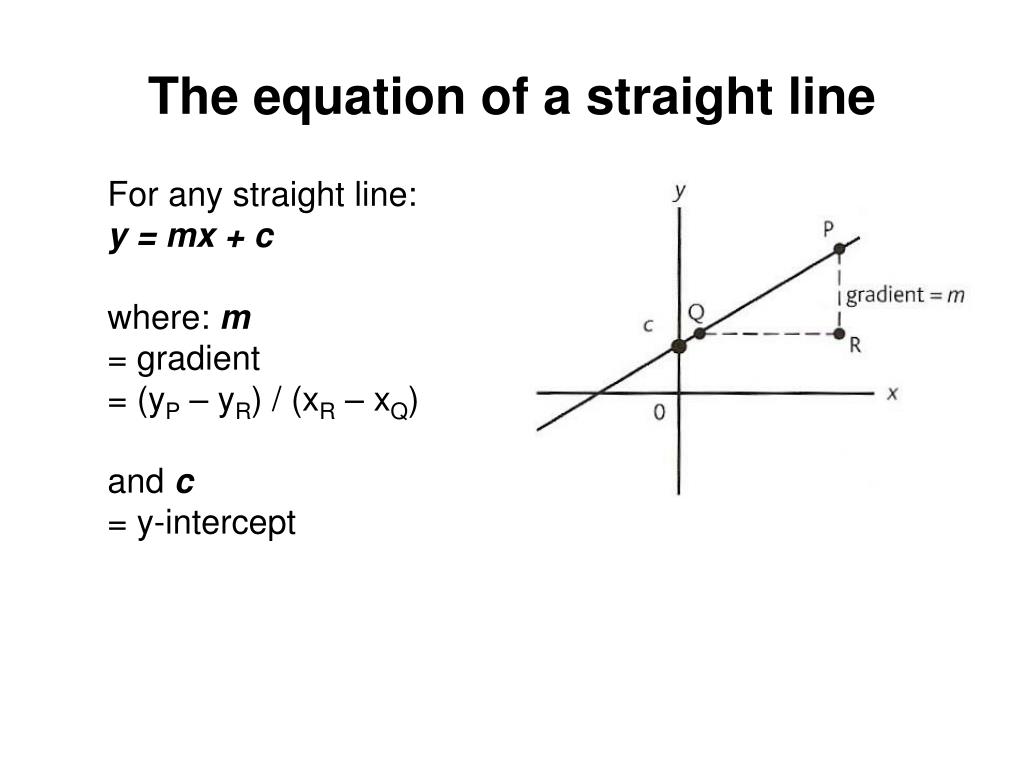
The equation that is written as y = mx c represents a straight line graph At any place on the horizontal (or "x") axis the line passes through a particular place on the other (vertical, or "y"). Earlier in this chapter we have expressed linear equations using the standard form Ax By = C Now we're going to show another way of expressing linear equations by using the slopeintercept form y = mx b In the slopeintercept form you use the slope of the line and the yintercept to express the linear function. These forms (see Linear equation for other forms) are generally named by the type of information (data) about the line that is needed to write down the form Some of the important data of a line is its slope, xintercept, known points on the line and yintercept.
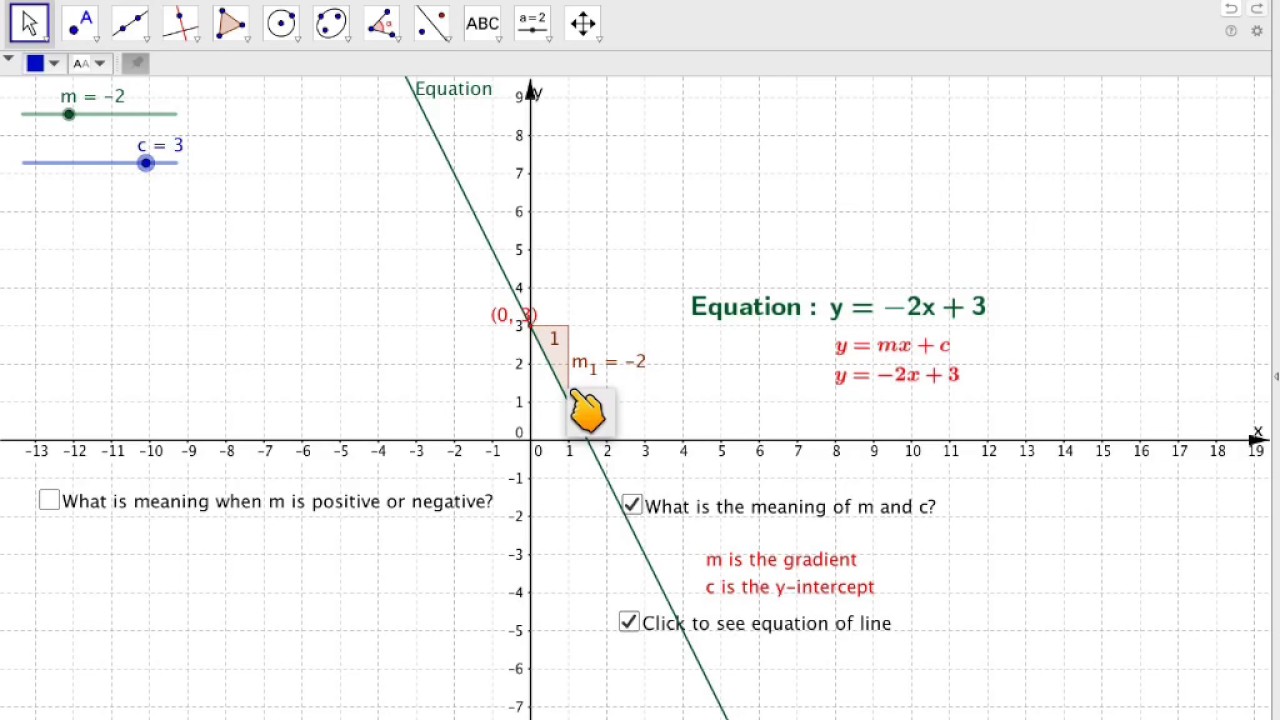
Explore the graph of the general linear equation in two variables that has the form a x b y = c using an applet by changing parameters a, b and c The properties of the line such as slope and x and y intercepts are also explored The investigation is carried out by changing the coefficients a, b, and c and analyzing their effects on the. Equation of a Straight Line The equation of a straight line is usually written this way y = mx b (or "y = mx c" in the UK see below). Equation of the form y = mx c, where m is the gradient and c is the yintercept Example Find the equation of the line with gradient 3 and yintercept 4 Here m = 3 and c = 4 We substitute the values of m and c into the equation to obtain y = 3x 4 Exercise Find the equations of the straight lines with the following gradients and yintercepts 1.
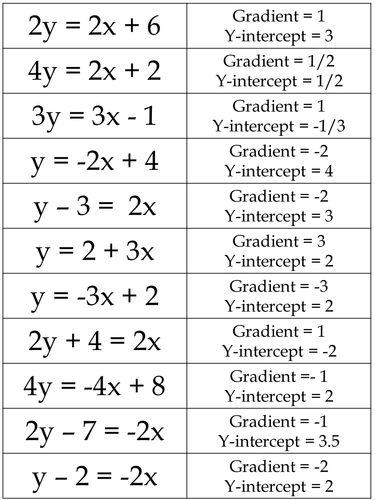
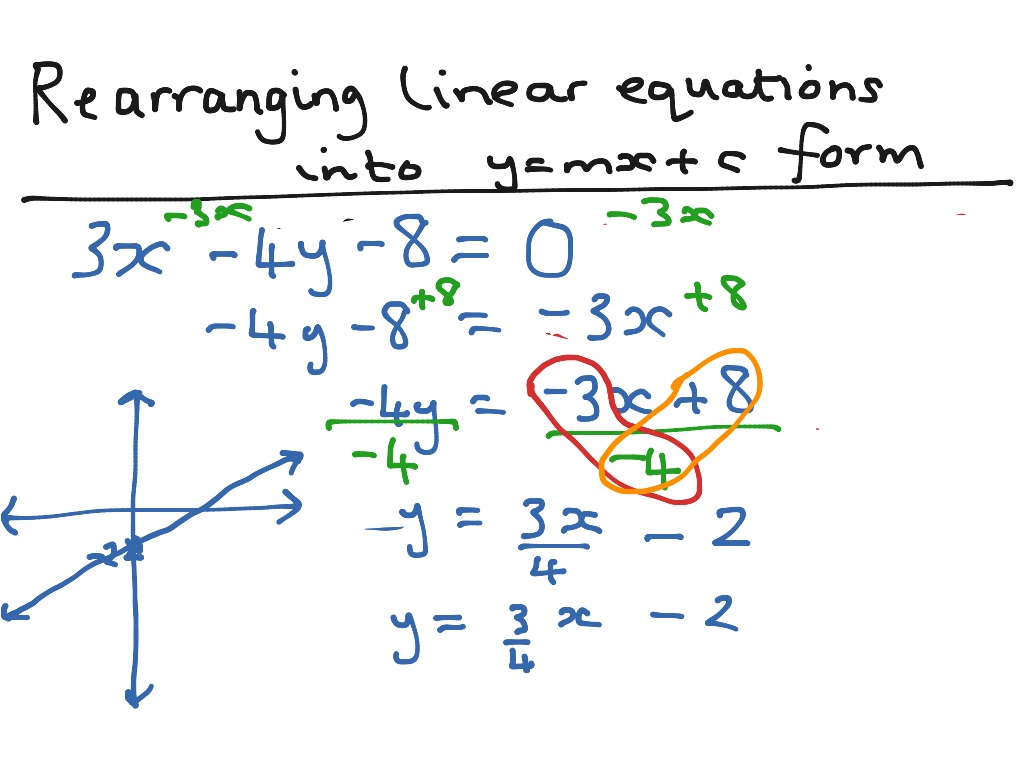
Skill 3 Rearranging Equations into the form y=mxc It is often necessary to rearrange the equation of a line to get it in the form y=mxc This is essential for finding the gradient and yintercept Example Find the gradient and yintercept of the line x2y=14 We want to rearrange this equation to make y the subject. These forms (see Linear equation for other forms) are generally named by the type of information (data) about the line that is needed to write down the form Some of the important data of a line is its slope, xintercept, known points on the line and yintercept. C is the intersect on the yaxis ie a constant value or Ax By C = 0;.
Remember the structure of y=mxb and that graphing it will always give you a straight line **There are MANY ways to. Match together equations and lines Know the formula y = mx c and understand that m = gradient and c = yintercept Match graphs of straight lines to their equations eg If you have 3 straight line graphs drawn, match them to y = 2x1, yx = 4, y = 3x5. A linear equation forms a straight line on the graph A nonlinear equation forms a curve on the graph The general form of linear equation is, y = mx c Where x and y are the variables, m is the slope of the line and c is a constant value The general form of nonlinear equations is, ax2 by2 = c.
B = where the line intersects the yaxis. Public Domain The equation y= mxc y = m x c represents a straight line graphically, where m m is its slope/gradient and c c its intercept In this tutorial, you will learn how to plot y= mxb y = m x b in Python with Matplotlib Consider the straight line y =2x1 y = 2 x 1, whose slope/gradient is 2 2 and intercept is 1 1 Before we plot, we need to import NumPy and use its linspace () function to create evenlyspaced points in a given interval. Y = mx c is an important reallife equation The gradient, m, represents rate of change (eg, cost per concert ticket) and the yintercept, c, represents a starting value (eg, an admin fee).
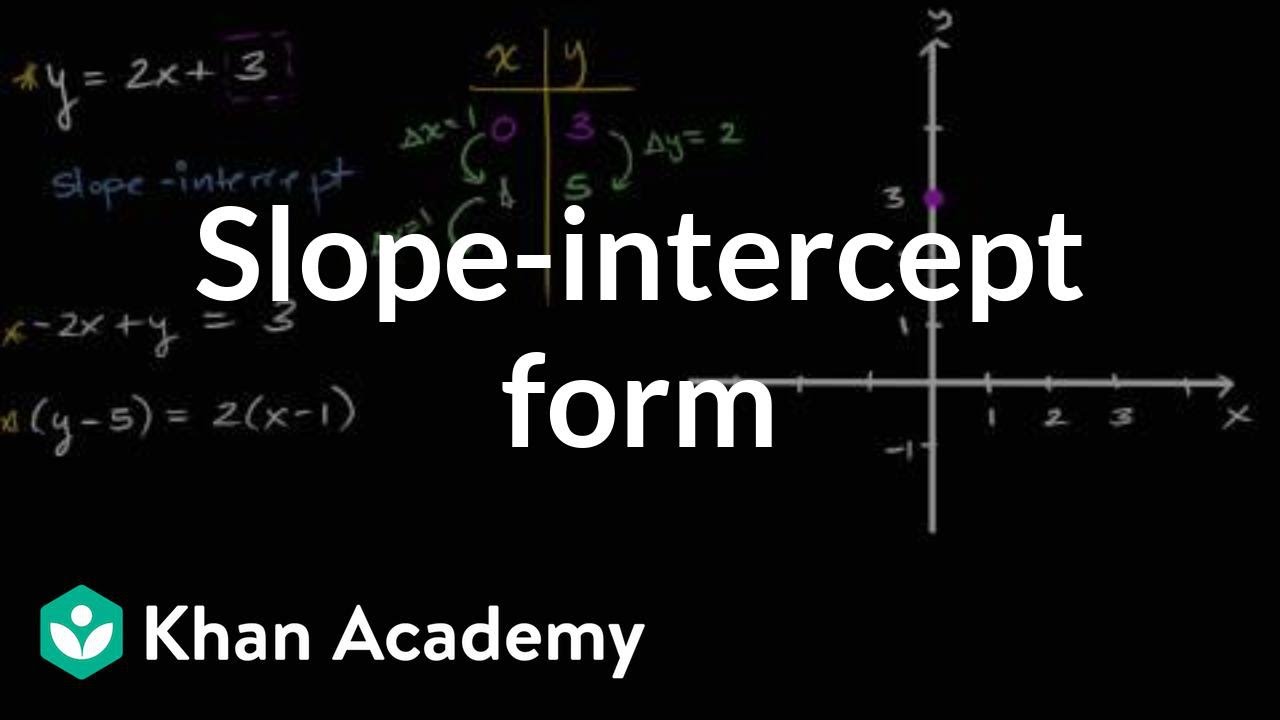
PAP Notes 23 Graph linear inequalities A linear inequality is written either in standard form or in slopeintercept form, and instead of an =, it has a , If you must solve the inequality for y, remember one important rule If you divide or multiply by a negative When drawing a linear inequality, you plot the points the same way as if it was an equation. We're asked to convert these linear equations into slopeintercept form and then graph them on a single coordinate plane We have our coordinate plane over here And just as a bit of a review, slopeintercept form is a form y is equal to mx plus b, where m is the slope and b is the intercept That's why it's called slopeintercept form. This activity is great for students to practice working on y = mx c in their own time, and could be set as a homework to consolidate work done in class However, the real power of this activity is to project it (preferably on an interactive board), and when you have got a random equation, get pupils to come to the front to move the points to.
Solution Steps y = m x c = y = mx c = Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side mxc=y mx c = y Subtract mx from both sides Subtract mx from both sides. Proportional and linear functions are almost identical in form The only difference is the addition of the “ b ” constant to the linear functionIndeed, a proportional relationship is just a linear relationship where b = 0, or to put it another way, where the line passes through the origin (0, 0)So a proportional relationship is just a special kind of linear relationship, ie, all. Linear law describes the relationship between two variables, X and Y and are related by the linear equation Y = MX C, where M is the gradient of the straight line and C, the Yintercept Using linear and quadratic functions to teach number patterns in secondary school.
Example 1 Write the equation of the line in slopeintercept form with a slope of \,5 and a yintercept of 3 The needed information to write the equation of the line in the form y = mx b are clearly given in the problem since m = \,5 (slope) b = 3 (yintercept) Substituting in y = mx b, we obtain. MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 Linear Equations in Two Variables with Answers MCQs from Class 9 Maths Chapter 4 – Linear Equations in Two Variables are provided here to help students prepare for their upcoming Maths exam In equation, y = mxc, m is a) Intercept b) Slope of the line c) Solution of the equation d) None of the. Linear functions are functions that produce a straight line graph The equation for a linear function is y = mx b, Where m = the slope ,;.
8) m = 8 0 4 ( 9) = 8 5 = 8 5 b = 0 (8 5. Y = mx c Any equation that can be rearranged into the form \ (y = mx c\), will have a straight line graph \ (m\) is the gradient, or steepness of the graph, and \ (c\) is the \ (y\)intercept,. Proportional and linear functions are almost identical in form The only difference is the addition of the “ b ” constant to the linear functionIndeed, a proportional relationship is just a linear relationship where b = 0, or to put it another way, where the line passes through the origin (0, 0)So a proportional relationship is just a special kind of linear relationship, ie, all.
For a linear function is y = mx b, Where m = the slope , x = the input variable (the “x” always has an exponent of 1, so these functions are always first degree polynomial ) b = where the line intersects the yaxisUnit 3 Linear Functions Equations And Their Algebra –. A linear equation forms a straight line on the graph A nonlinear equation forms a curve on the graph The general form of linear equation is, y = mx c Where x and y are the variables, m is the slope of the line and c is a constant value The general form of nonlinear equations is, ax2 by2 = c. Telling the slope of a line from its graph;.
To convert from y = mxb to axbyc = 0 we only have to move everything to one side by subtracting terms Ex/ y = 3x2 converts to y3x2 = 0 (We subtracted 3x and 2 from both sides of the equation) To convert from axbyc = 0 to y = mxb we need only to solve for y Ex/ 4x2y6 = 0 converts to 2y = 4x6 then dividing by 2 gives y = 2x3 Tyler. Linear Equations (C) Answers Use the given points to determine the slope using y 2{y 1 x 2{x 1 Determine the yintercept using b = y mx Write the equation in y = mxb form 1Points (0;. Know the formula y = mx c and understand that m = gradient and c = yintercept Work out the gradient and yintercept from the equation of a line without the graph eg What is the gradient and yintercept of the line y = 4x2 Match together equations and lines Know the formula y = mx c and understand that m = gradient and c = yintercept.
Linear equations are equations of the first order These equations are defined for lines in the coordinate system An equation for a straight line is called a linear equation The general representation of the straightline equation is y=mxb, where m is the slope of the line and b is the yintercept Linear equations are those equations that are of the first order. M is the slope of the straight line;. 4) (2;1) m = 1 ( 4) 2 0 = 5 2 = 5 2 b = 4 5 2 (0) = 4 y = 5 2 x 4 2Points (8;9) ( 3;3) m = 3 9 3 8 = 6 11 = 6 11 b = 9 6 11 (8) = 4 7 11 y = 6 11 x4 7 11 3Points ( 9;0) ( 4;.
The slopeintercept form of a linear equation is y = mx b, where x and y are coordinates of an ordered pair, m is the slope of the line, and b is where the line crosses the yaxis Which is an equivalent equation solved for the slope, m?. Often linear equations are written in standard form with integer coefficients (A x B y = C) Such relationships must be converted into slopeintercept form (y = mx b) for easy use on the graphing calculator One other form of an equation for a line is called the pointslope form and is as follows y y1 = m (x x1). Linear Equation Formula is given by y = mx c Where x and y are two variables, c is a constant and m is the slope of the equation Solved Examples Using Linear Equation Formula.
The equation that is written as y = mx c represents a straight line graph At any place on the horizontal (or "x") axis the line passes through a particular place on the other (vertical, or "y"). X = the input variable (the “x” always has an exponent of 1, so these functions are always first degree polynomial);. Y = mx c, m ≠ 0 Linear Equation Formula Some general formulas are Slop Intercept Form Point Form Two Point Form Examples of Linear Equations In above examples, the highest exponent of the variable is 1 Equation with one Variable An equation having one variable, eg 12x – 10 = 0;.
Telling the slope of a line when given two points on it. Solution Steps y = m x c = y = mx c = Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side mxc=y mx c = y Subtract mx from both sides Subtract mx from both sides.
Rearrange Eqn Into Y Mx C Form Math Algebra Linear Functions Showme

Prove E Squareroot M From Linear Equation Y Mx Chegg Com

Graphical Analysis Of One Dimensional Motion Physics
Linear Equation Ymx+c のギャラリー
Linear Equation Wikipedia

Gradient Slope Intercept Form Passy S World Of Mathematics
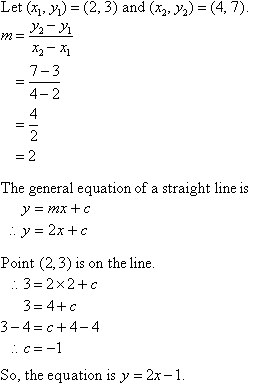
Equation Of A Straight Line
Plotting Straight Line Graphs Mr Mathematics Com

Intercepts Y Mx C Variation Theory

Write The Linear Equation Ax By C In The Form Y Mx Basap Pls Brainly In
Q Tbn And9gcrezv8ztdpevhpccdn7nmrclkbgs6g9cjusdu0et7mivd91tq Usqp Cau

Equation Of A Straight Line

The Straight Line
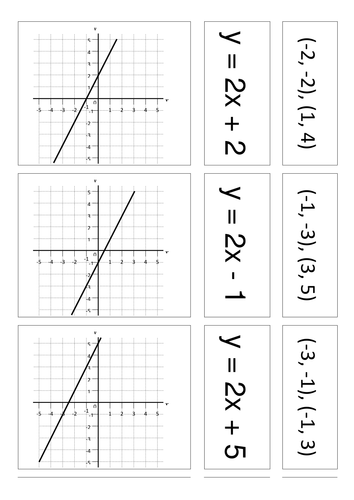
Y Mx C Match Cards Teaching Resources

Draw Graph Of The Linear Equation F Mx C For M 2 And C 1 Read The Value Of Y If Math Linear Equations In Two Variables Meritnation Com

Straight Lines S Cool The Revision Website

If The Straight Line Y Mx C Passes Through The Points 2 4 And 3 6 Find The Values Of M And C

Linear Graphs
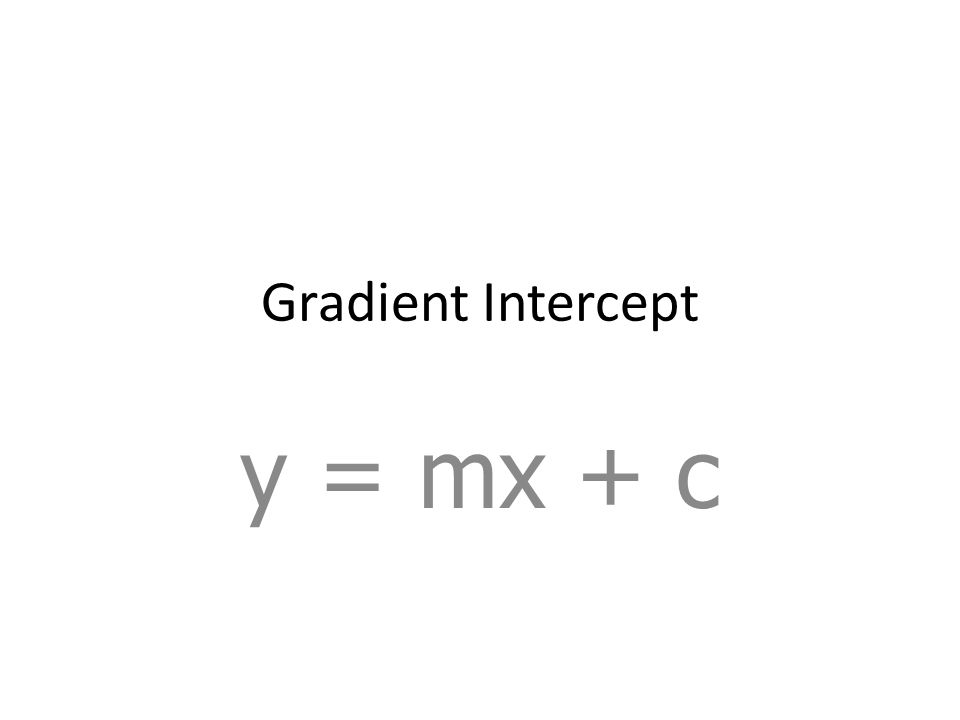
Gradient Intercept Y Mx C Gradient Of A Line Graphs Y Mx C X Y Y Intercept Where The Graph Cuts The Y Axis Gradient The Slope Steepness Of Ppt Download

2 5 C General Linear Graph Form Linear Graphs Edexcel Gcse Maths Foundation Elevise
Q Tbn And9gctxl4gvodwjgxazrj3yjrxvqm8utzfs3venblardl D0sur0qlf Usqp Cau
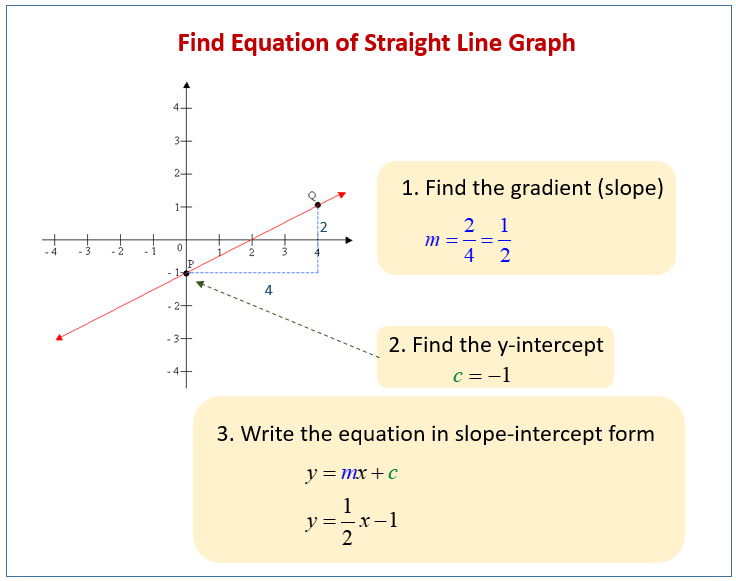
Equation Of Straight Line Graphs Solutions Examples Videos Worksheets Games Activities

Learning Task 2 A Write The Linear Equation Ax By C In The Form Y Mx B 1 3x 4y 8 2 10x Brainly Ph

Draw The Graph Of A Linear Equation Y Mx C For M 2 And C 1 Read The Graph The Value Of Y Math Linear Equations In Two Variables Meritnation Com

Intercepts Y Mx C Variation Theory
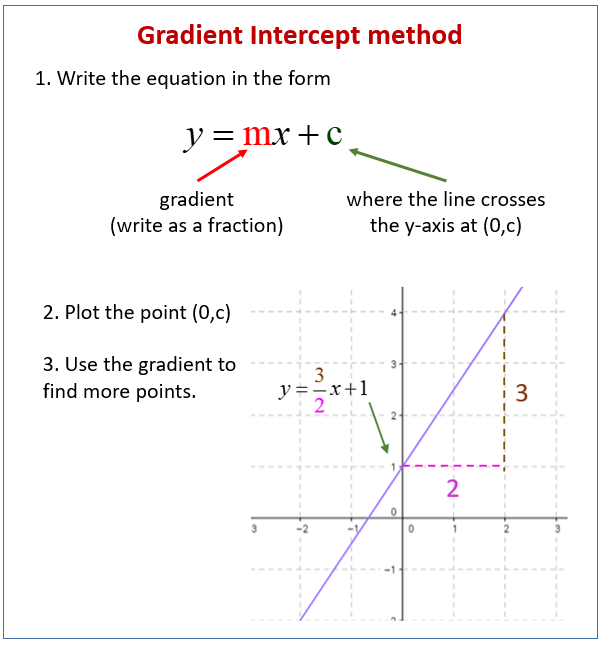
Straight Line Graphs Examples Videos Worksheets Solutions Activities

Write The Linear Equation Y Mx B In The Form Ax By C With Solution Po Sana Brainly Ph
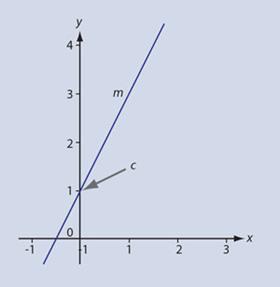
Using The Equation Of A Straight Line Maths Rsc Education
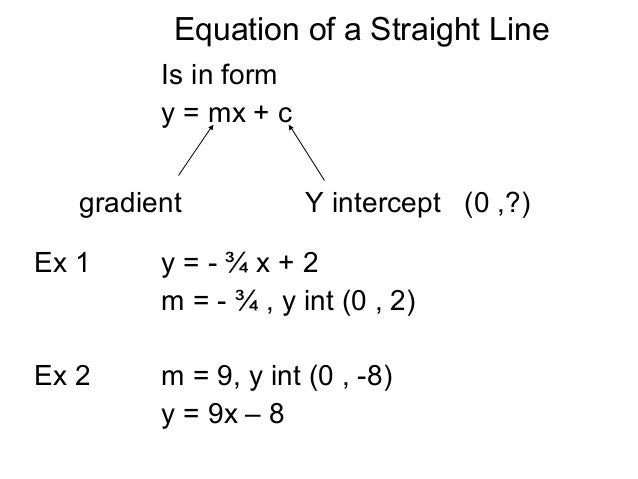
Y Mx C

The Line Of The Equation Y Mx C Passes Through The Points 1 4 And 2 5 Determine The Values Of M And C
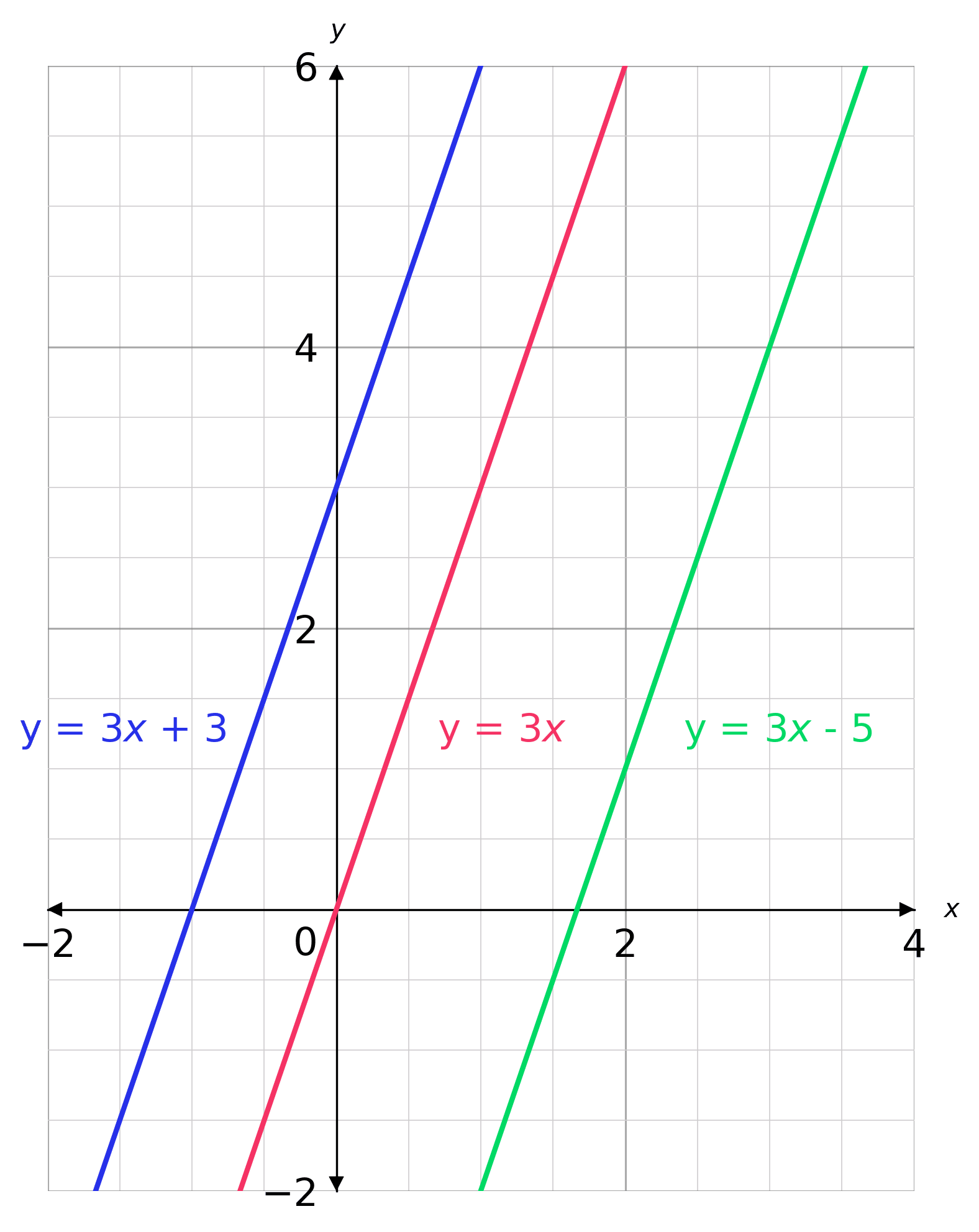
Parallel And Perpendicular Lines Worksheets Questions And Revision
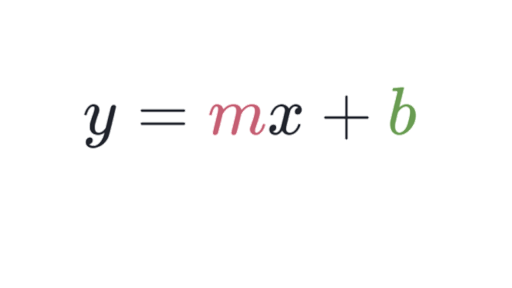
Slope Intercept Form Introduction Algebra Article Khan Academy
What Is The Graph Of Y Mx C Quora
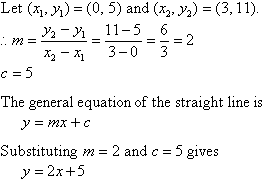
Equation Of A Straight Line
3
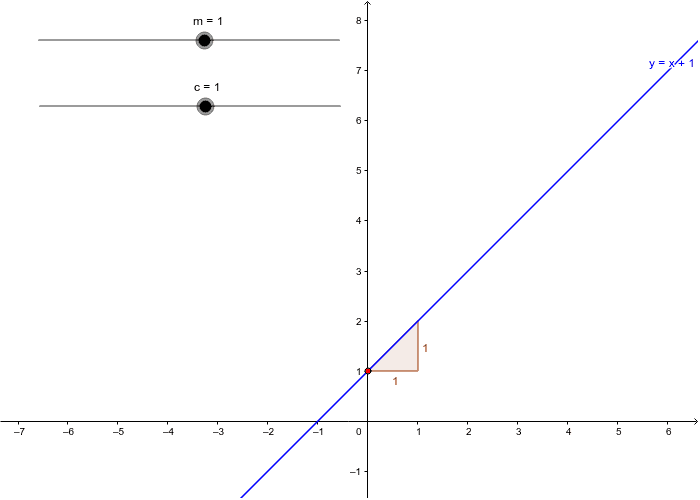
Graphing Linear Equations Y Mx C Geogebra

2 5 H Y Intercept Linear Graphs Edexcel Gcse Maths Foundation Elevise

Exercise Worksheet For Converting A Linear Equation From General To Slope Intercept Form

Y Mx C Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme
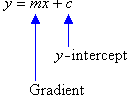
Equation Of A Straight Line
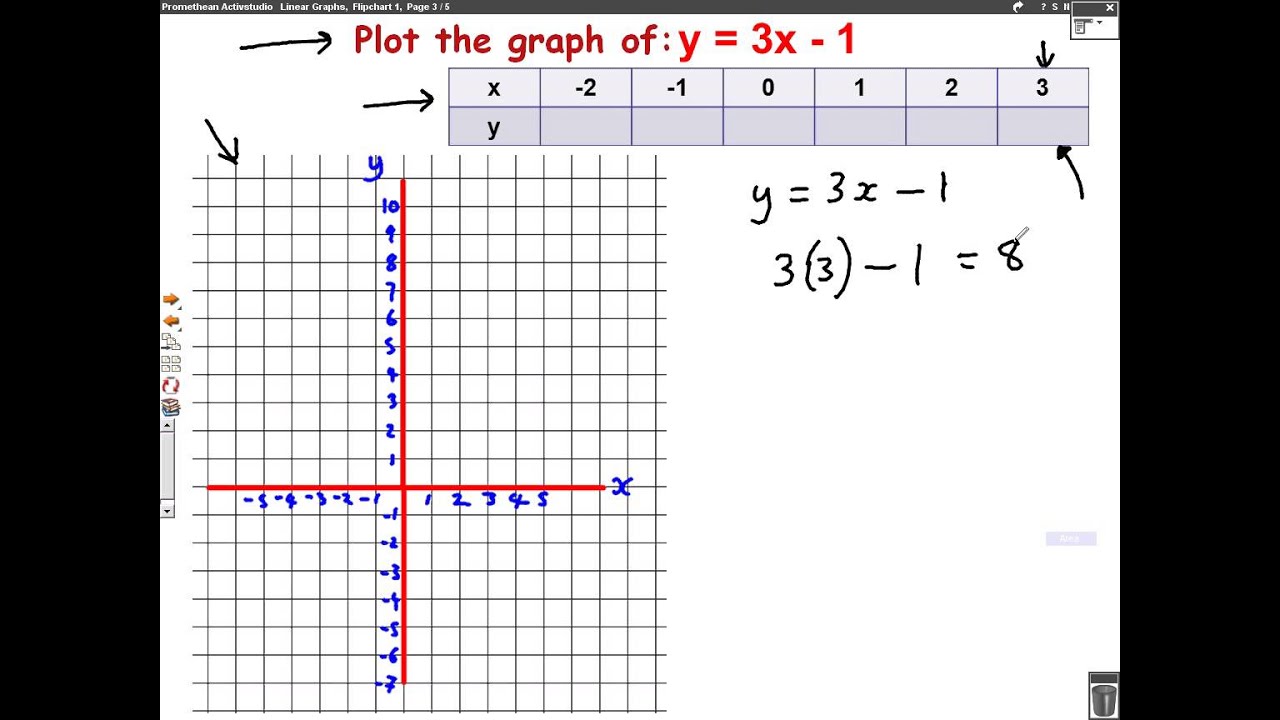
Plotting Graphs Y Mx C Mathscast Youtube
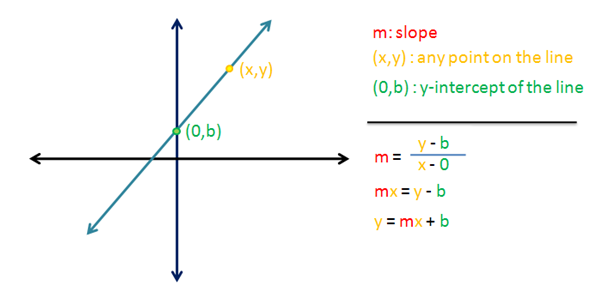
Equation Of A Line The Derivation Of Y Mx B
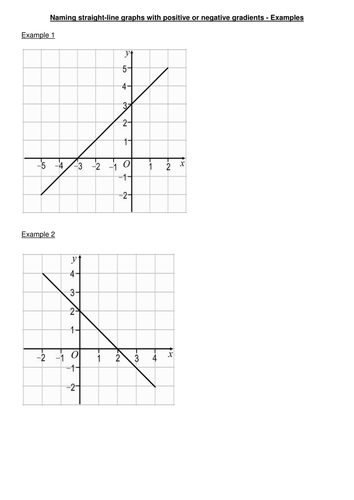
Y Mx C Teaching Resources

Analyzing The Effects Of The Changes In M And B On The Graph Of Y Mx B Texas Gateway
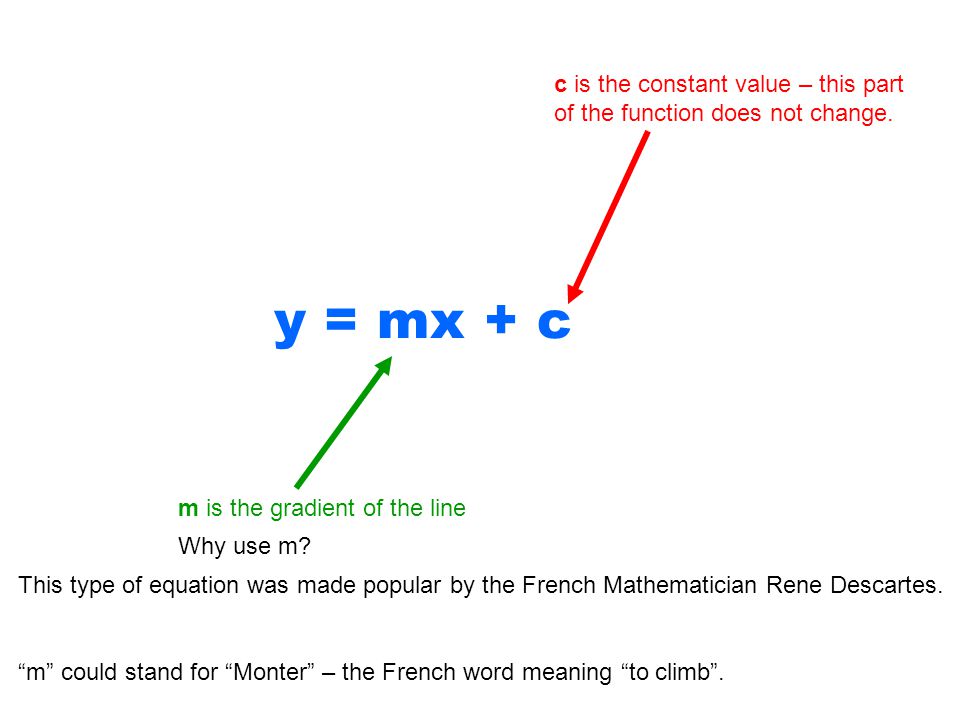
Objective Understand That All Straight Line Graphs Can Be Represented In The Form Y Mx C And Be Able To State The Equation Of Given Graphs Ppt Video Online Download

Unit 5 Section 2 Straight Line Graphs

Lesson 3 See Lesson Plans

Intercepts Y Mx C Variation Theory
Understanding Y Mx C
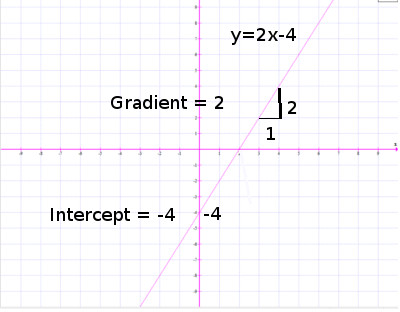
Y Mx C Maths With Graham

Draw The Graph Of The Linear Equation Y Mx C For M 2 C 5 And Read The Value Of Y When X 3 2 Math Linear Equations In Two Variables Meritnation Com

Exercise Worksheet For Linear Equations In Slope Intercept Form
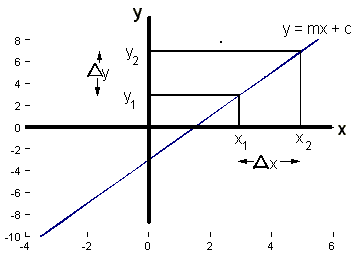
4 Basic Differentiation
The Equation Of A Straight Line Graph Y Mx C Youtube
Linear Regression Basic Machine Learning By Jacob S Medium
Prove That The Equation Of A Line With Slope M And Y Intercept Y Mx C Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
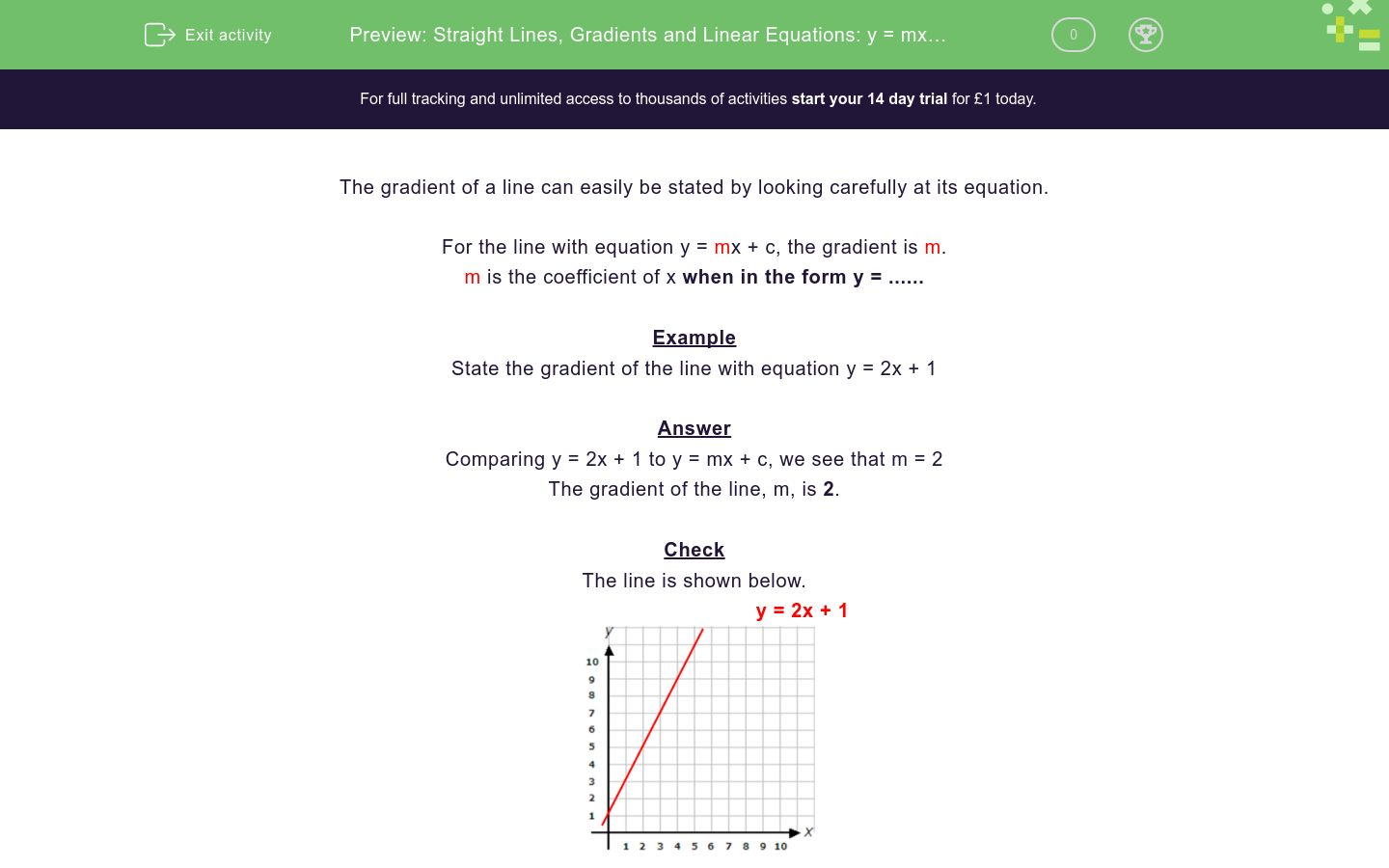
Straight Lines Gradients And Linear Equations Y Mx C Worksheet Edplace
Gce A Level Physics G5 Data Analysis Using Y Mx C Youtube
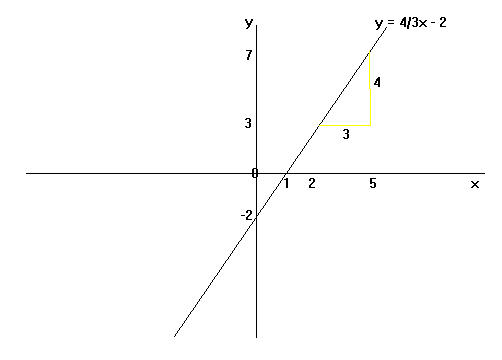
Equation Of A Straight Line Maths Gcse Revision
Intro To Slope Intercept Form Y Mx B Algebra Video Khan Academy

Misc 13 Equation Of Line Passing Through Origin Making Angle
/LinearRelationshipDefinition2-a62b18ef1633418da1127aa7608b87a2.png)
Linear Relationship Definition

In The Linear Equation Y Mx B Why Is That The Slope Multiplied By The X Coordinate Plus The Y Intercept Gives Us The Y Coordinate Quora
Q Tbn And9gcqzytqumfhv Ha8bt9t4khclv6gdr0sqzjldpinmxr9eyaadhnn Usqp Cau

Formula For Linear Equations By Country Xpost R Mapporn Math

Linear Further Maths U3 4
Y Mx C Geogebra
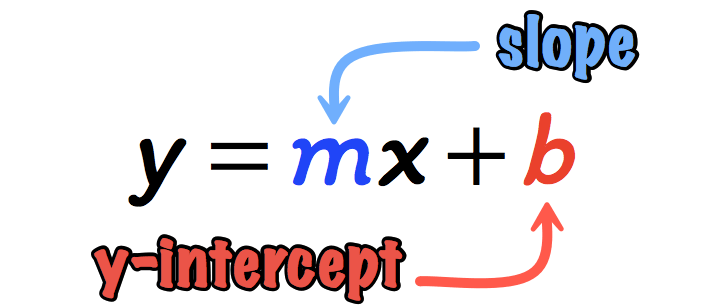
Slope Intercept Form Of A Straight Line Y Mx B Chilimath

Y Mx C Teaching Resources
Interpret Linear Regression In 10 Mins Non Technical By Anish Mahapatra Towards Data Science
Y Mx C Equation Of A Line Youtube
How To Find The Equation Of A Straight Line Y Mx C Youtube
Ppt The Equation Of A Straight Line Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
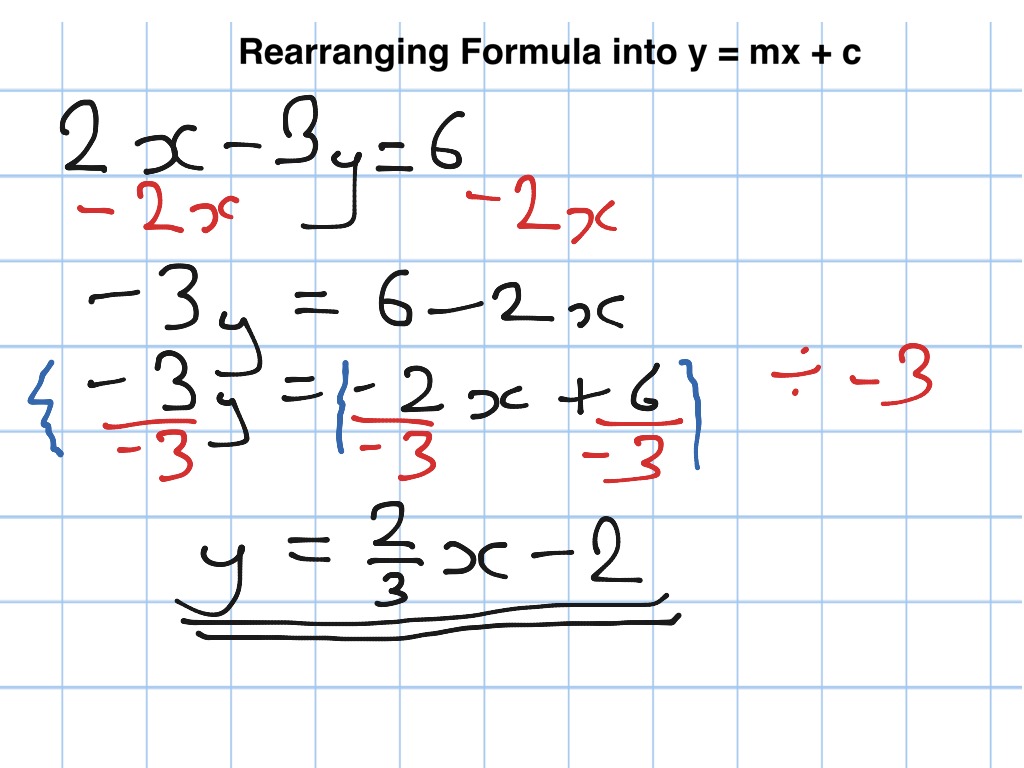
Rearranging Into Y Mx C Math Algebra Linear Functions Slope Intercept Form Showme
What Is The Graphical Representation Of The Equation Y Mx C Quora

How To Graph Linear Equations Using Y Mx B Math Wonderhowto
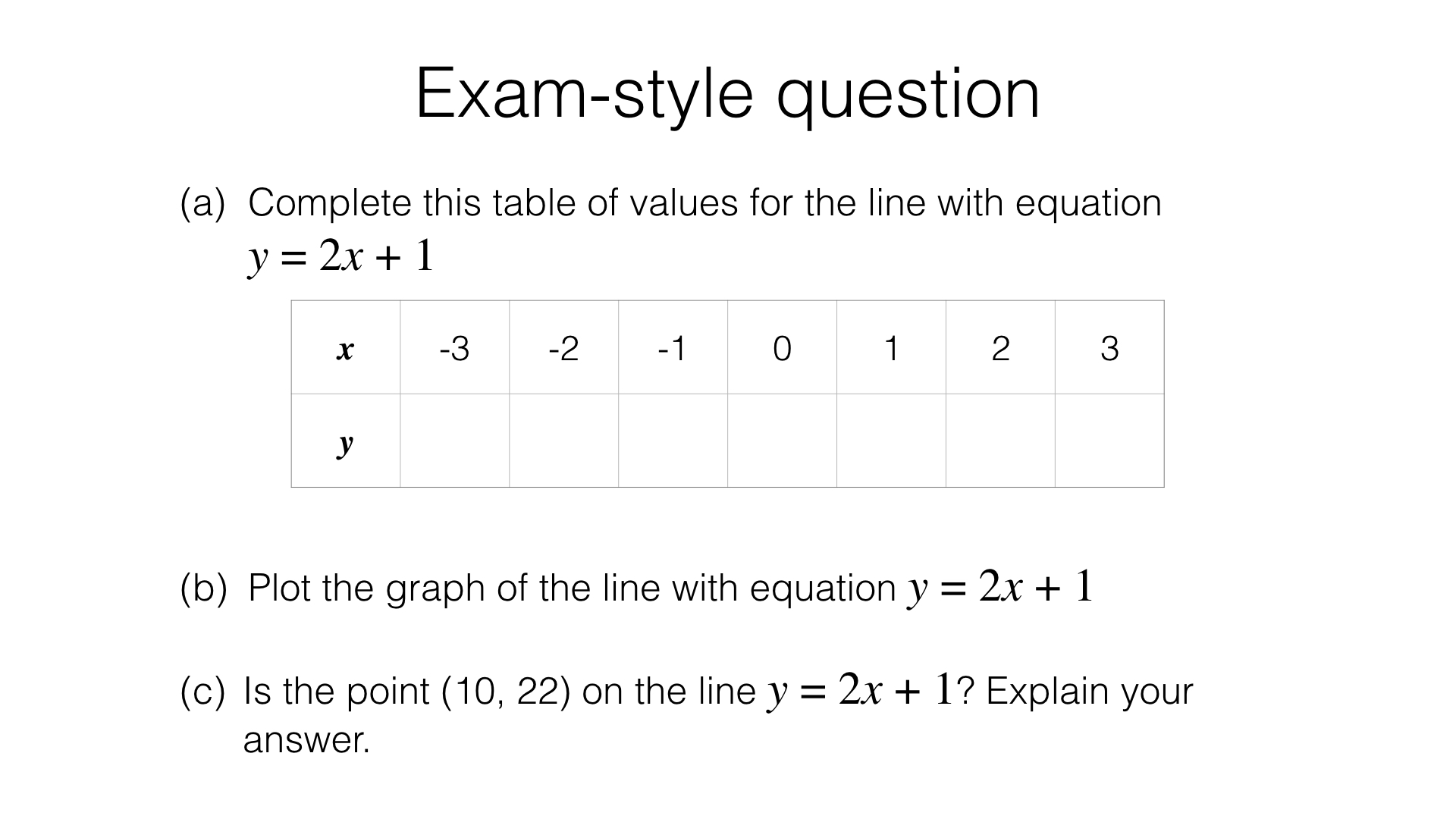
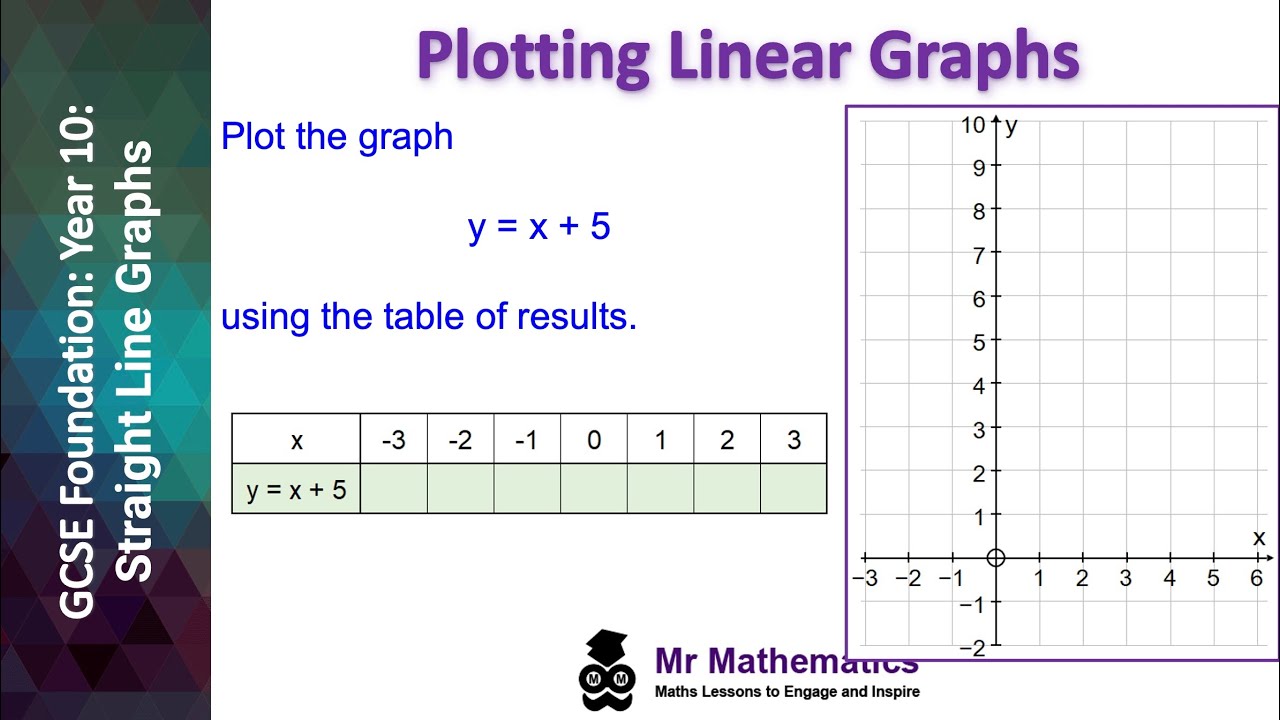
a Plotting Straight Line Graphs Bossmaths Com
What Is Y Mx C Quora

Linear Relationship Rules Passy S World Of Mathematics

Equation Of Straight Line Graphs Mr Mathematics Com
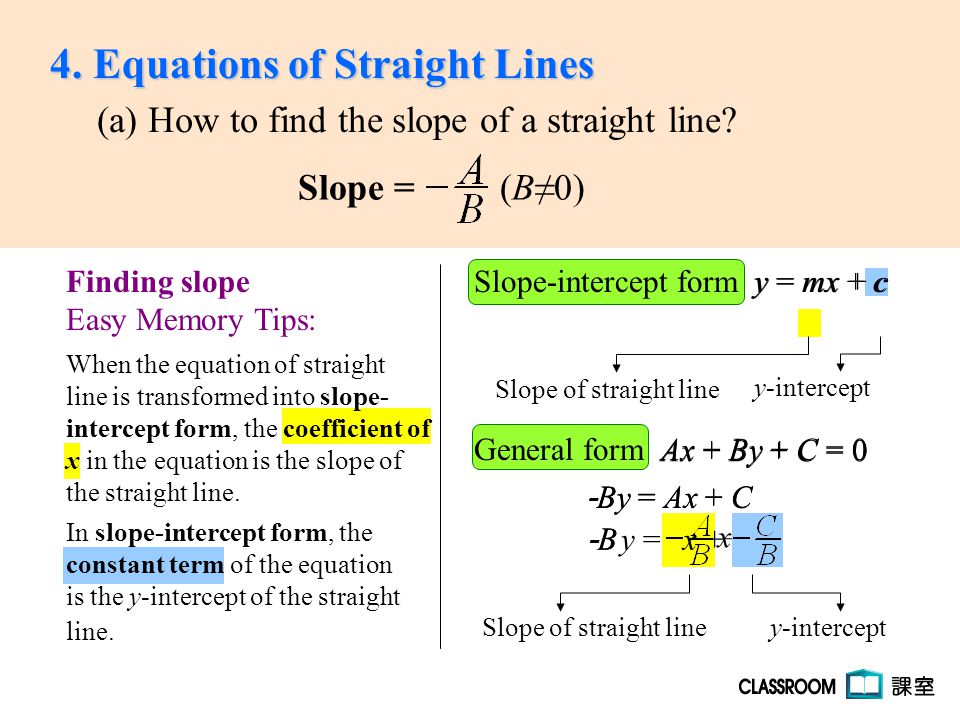
Slope Intercept Form Y Mx Cy Mx C General Form Ax By C 0 In Slope Intercept Form The When The Equation Of Straight Ac A How To Find The Ppt Download

Straight Line Graphs Objective Understand That All Straight Line Graphs Can Be Represented In The Form Y Mx C And Be Able To State The Equation Of Given Ppt Download

New Calibration With Offset And Y Mx C Linear Equation Methods Download Scientific Diagram
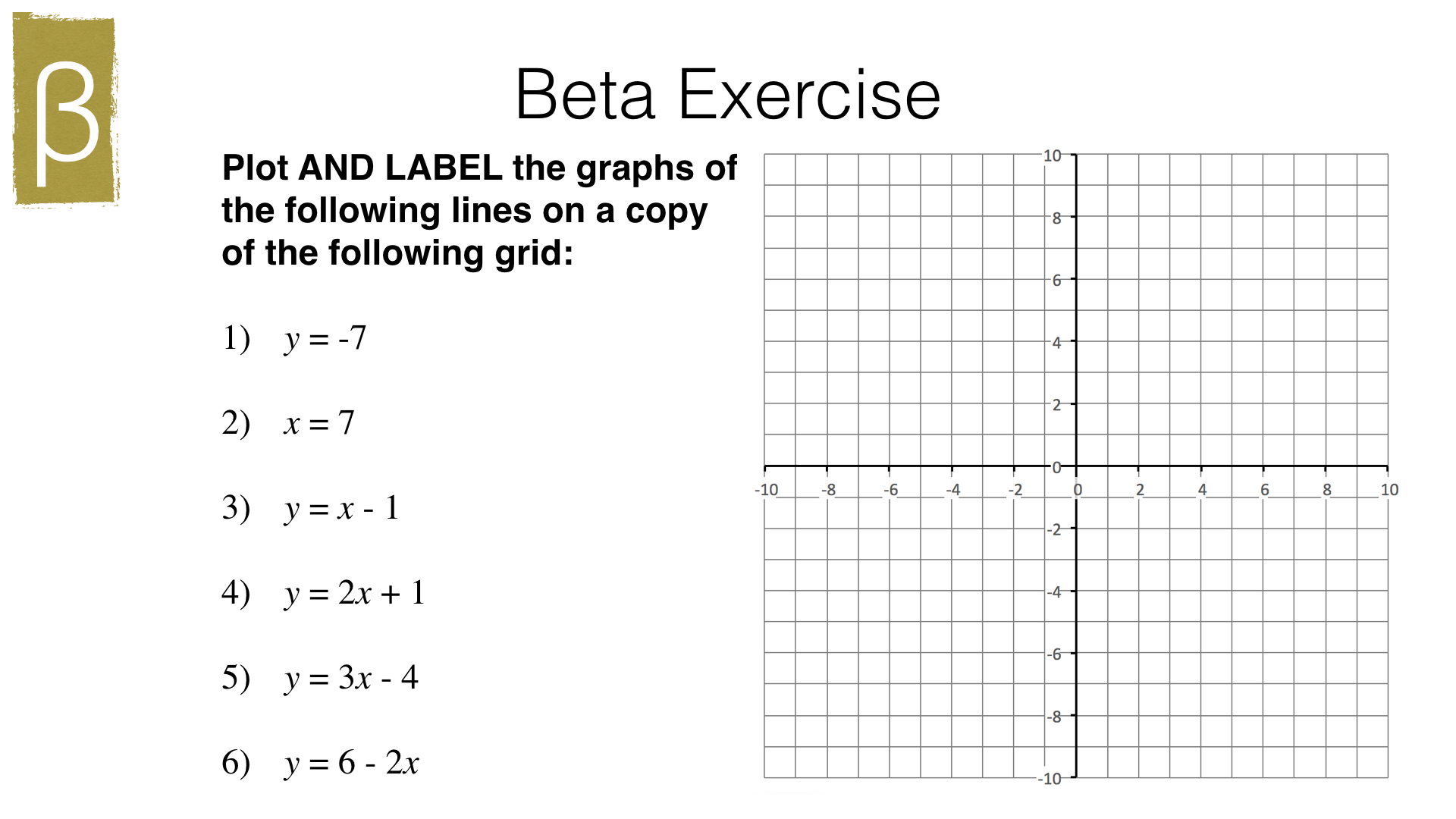
a Plotting Straight Line Graphs Bossmaths Com
Plenary The Equation Of A Straight Line
Solution What Does The Equation Y Mx C Mean

Equation Of A Line Textbook Exercise Corbettmaths

Equation Of A Straight Line

Finding The Equation Of Straight Line Graphs Mr Mathematics Com

Using The Equation Of A Straight Line Maths Rsc Education
Solved C A Be 10 In The Xy Plane The Graph Of A Line Chegg Com
Linear Graphs Revise Algebra Gcse Maths Tutor

Straight Line Graphs Revision Session How To Draw A Line Using Y Mx C Parallel Lines Ppt Download

Rearranging Linear Equations Into The Form Y Mx C Teaching Resources
Graphing Linear Function Linear Function F X Mx C

Equation Of A Straight Line

Draw A Graph Of Linear Equation Y Mx C For M 2 And C 1 Read From The Graph The Value Of When X 3 2 Math Linear Equations In Two Variables Meritnation Com

Data Science Linear Regression
New Stack

Illustrate The Ic 50 Value Of Desmostachysbipinnata From The Linear Download Scientific Diagram

Rearranging Formula Into Y Mx C Tutorial Youtube
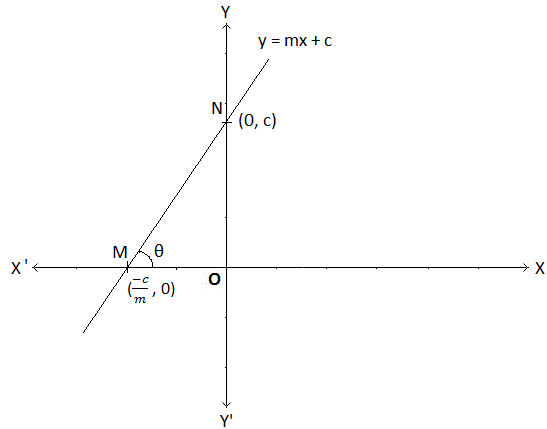
Slope Of The Graph Of Y Mx C What Is The Graph Of Y Mx C

What Is The Condition For A Straight Line To Pass Through The Origin Quora
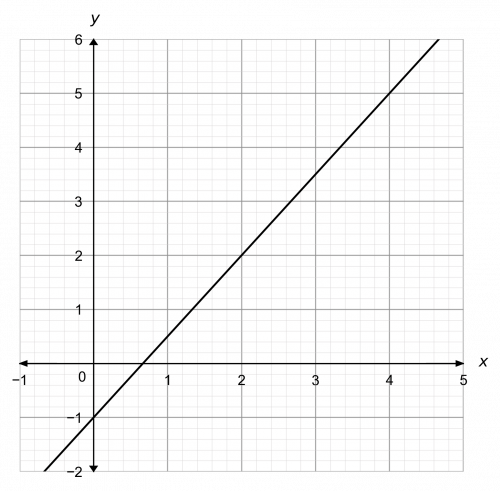
Y Mx C Worksheets Questions And Revision Mme

Y Mx C Video Corbettmaths




